Introduction to Nerve Ultrasound in Paresthesia Diagnosis
Nerve Ultrasound: A New Frontier in Paresthesia Diagnosis is transforming how we approach nerve-related issues. As more patients experience unexplained tingling, numbness, or pain—commonly known as paresthesia—the demand for precise diagnostic methods has never been higher. Traditional techniques like electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies have served us well, but they come with limitations that can hinder accurate diagnoses.
Enter nerve ultrasound—a non-invasive imaging technique that offers a fresh perspective on nervous system health. By visualizing nerves in real-time, this innovative method empowers healthcare professionals to pinpoint the exact causes of paresthesia more effectively than ever before. Patients can now look forward to faster diagnoses and tailored treatment plans designed just for them.
Join us as we delve deeper into the world of nerve ultrasound and explore how it’s reshaping diagnostics for those suffering from mysterious nerve sensations. Discover its workings, benefits over traditional methods, procedural insights, and what you can expect if your physician recommends it.
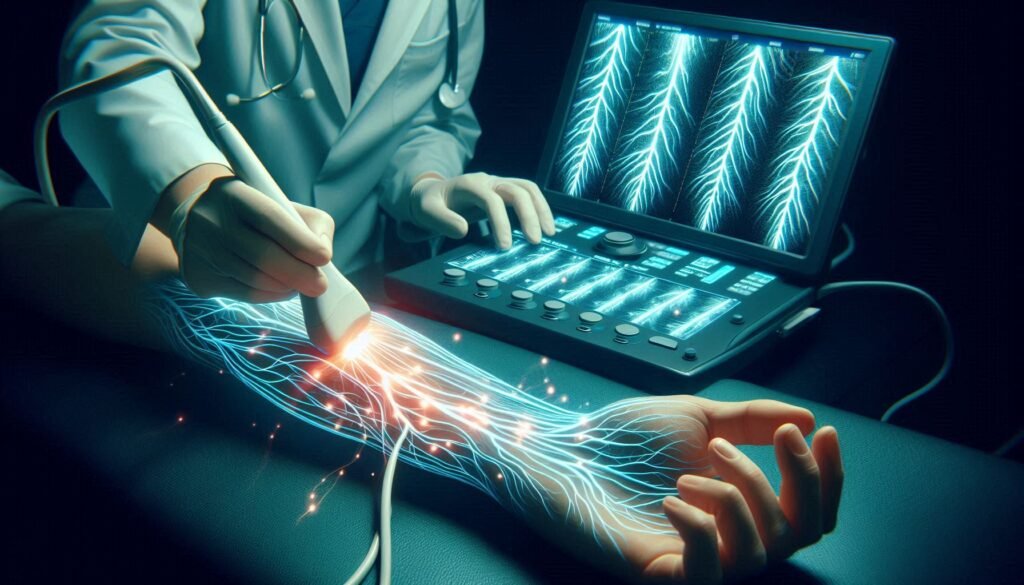

How Nerve Ultrasound Works: Visualizing Nerve Structures
Nerve ultrasound is a cutting-edge imaging technique that utilizes high-frequency sound waves to visualize nerve structures in real time. Unlike traditional imaging methods, this approach allows for detailed visualization of peripheral nerves, revealing their size and shape.
During the procedure, a transducer emits sound waves that penetrate the skin and bounce back after hitting nerve tissues. The returning echoes are converted into images by specialized software. This process creates a dynamic view of not only the nerves but also surrounding tissues.
Health practitioners can observe any abnormalities such as swelling or compression directly on the screen. This immediate feedback enables quicker diagnostic decisions when assessing conditions related to paresthesia.
Moreover, nerve ultrasound is non-invasive and free from radiation exposure. Patients experience minimal discomfort during the examination, making it an appealing option for those seeking answers about their symptoms without invasive measures.
Advantages of Nerve Ultrasound Over Traditional Diagnostic Methods
Nerve ultrasound offers several advantages over traditional diagnostic methods, making it a game changer in paresthesia diagnosis. First and foremost, this non-invasive technique allows for real-time visualization of nerve structures. Clinicians can assess the size, shape, and integrity of nerves without resorting to more invasive procedures.
Another significant benefit is its ability to provide dynamic imaging. Unlike static tests such as MRI or CT scans, nerve ultrasound captures movement and changes in real time. This capability helps identify compression or entrapment issues that may cause symptoms like tingling or numbness.
Additionally, nerve ultrasound is widely accessible and cost-effective compared to other imaging modalities. Patients often experience shorter wait times for appointments and results.
This technology reduces the need for unnecessary surgical interventions by accurately identifying underlying conditions earlier on in the patient’s journey. As a result, patients receive targeted treatment options based on precise diagnoses rather than relying solely on trial-and-error approaches.
When is Nerve Ultrasound Recommended for Paresthesia?
Nerve ultrasound is recommended in specific scenarios involving paresthesia. When patients experience unexplained sensations like tingling or numbness, this imaging technique can provide clarity. It’s particularly useful when symptoms suggest a nerve entrapment or compression.
If traditional tests such as EMG and nerve conduction studies yield inconclusive results, nerve ultrasound offers an alternative approach. This method helps visualize nerves directly, making it easier to identify structural abnormalities that may be causing discomfort.
Additionally, if there’s a suspicion of conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome or thoracic outlet syndrome, nerve ultrasound becomes invaluable. Clinicians often turn to this tool when they need real-time imaging to assess the integrity and morphology of peripheral nerves.
In cases where surgical intervention is being considered for pain relief due to suspected neuropathy, pre-operative assessments with nerve ultrasound can help guide decisions. Its ability to reveal precise anatomical details aids specialists in formulating effective treatment plans tailored for each patient.
The Nerve Ultrasound Procedure: What to Expect
If you’re scheduled for a nerve ultrasound, it’s important to know what the procedure entails. First, you’ll be asked to lie down comfortably in a position that allows easy access to the area being examined. The technician will apply a water-based gel on your skin. This gel helps transmit sound waves and provides clear images of the nerves.
Next, the technician uses a handheld device called a transducer. They will move this instrument over your skin while capturing real-time images of nerve structures beneath. You might feel slight pressure but should not experience any pain during this process.
The entire examination typically lasts around 30-45 minutes, depending on how many areas are assessed. It is non-invasive and generally safe with minimal risks involved.
After completing the imaging, you can usually resume your normal activities immediately. The results will then be interpreted by a specialist who will discuss findings with you at your follow-up appointment.
Interpreting Nerve Ultrasound Results: What They Reveal
Interpreting nerve ultrasound results requires a keen understanding of the images produced. These ultrasounds provide detailed visuals of nerve structures, allowing clinicians to identify abnormalities such as swelling, compression, or any structural changes. The clarity of these images often surpasses traditional imaging techniques.
Radiologists and neurologists look for specific markers in the ultrasound scans. Increased cross-sectional area may indicate conditions like entrapment syndromes or neuropathies. Conversely, reduced size can suggest atrophy or injury.
The assessment also includes evaluating the echogenicity—how reflective tissues appear on the screen—which can reveal inflammation or damage within nerve fibers. This information is crucial for forming an accurate diagnosis.
These insights enable healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans effectively. By pinpointing issues directly related to paresthesia symptoms, patients receive more personalized care that addresses their unique situations without unnecessary procedures.
Comparing Nerve Ultrasound to EMG and Nerve Conduction Studies
Nerve ultrasound, electromyography (EMG), and nerve conduction studies are essential tools in diagnosing paresthesia. Each technique has unique strengths that complement each other. Nerve ultrasound visualizes the anatomy of nerves directly, allowing clinicians to identify structural abnormalities such as swelling or compression.
In contrast, EMG assesses muscle activity by measuring electrical signals from motor neurons. This technique helps determine if there is an issue at the level of the nerve or muscle itself but doesn’t provide a direct view of nerve structure. Nerve conduction studies measure how fast electrical impulses travel along a nerve, highlighting issues with signal transmission.
While EMG and nerve conduction studies can indicate functional problems within nerves, they may miss subtle anatomical changes detected by ultrasound. By combining these methods, healthcare providers gain a comprehensive understanding of both structure and function in patients experiencing paresthesia.
The choice between these diagnostic tools depends on individual symptoms and clinical needs, making collaboration among specialists crucial for accurate diagnoses.
Limitations and Challenges of Nerve Ultrasound Technology
Despite its advantages, nerve ultrasound technology faces several limitations and challenges. One significant issue is the operator dependency of the procedure. The accuracy of results heavily relies on the skill and experience of the technician performing the ultrasound. An inexperienced operator may miss crucial details or misinterpret findings.
Another challenge lies in patient factors. Body habitus can affect image quality; for instance, obesity or excessive muscle mass makes it difficult to visualize nerves clearly. This variability can lead to inconsistent diagnostic outcomes across different patients.
Additionally, nerve ultrasound has a limited ability to assess certain conditions comprehensively. While it excels at visualizing structural abnormalities, it might not fully capture functional impairments as seen with electrophysiological studies.
Widespread adoption remains hampered by cost and accessibility issues. Not all medical facilities have access to advanced equipment or trained personnel proficient in interpreting nerve ultrasounds effectively. These barriers can inhibit timely diagnosis for many patients experiencing paresthesia.
Future Developments in Nerve Ultrasound for Paresthesia Diagnosis
The future of nerve ultrasound in paresthesia diagnosis holds immense promise. As technology advances, we can expect enhancements in imaging resolution and speed. This will allow healthcare providers to visualize nerve structures with even greater clarity, improving diagnostic accuracy.
Research is also underway to develop automated image analysis tools. These tools could help streamline the interpretation process by identifying abnormalities quickly and consistently. Such advancements may reduce the need for extensive training on complex image readings.
Moreover, integrating artificial intelligence into nerve ultrasound systems has the potential to revolutionize how we diagnose peripheral neuropathies. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, leading to more personalized treatment plans tailored specifically for each patient’s condition.
Increased collaboration among researchers and clinicians is essential for expanding the applications of nerve ultrasound beyond current uses. By sharing insights and findings, the medical community can pave new pathways toward innovative diagnostic solutions that enhance patient care.
Integrating Nerve Ultrasound into Your Diagnostic Journey
Integrating nerve ultrasound into your diagnostic journey can offer a fresh perspective on understanding paresthesia. It is essential to communicate openly with your healthcare provider about any symptoms you’re experiencing. If traditional methods haven’t provided clarity, discussing the possibility of nerve ultrasound might be beneficial.
This technology allows for real-time visualization of nerves, making it easier to identify abnormalities that could contribute to your sensations. As more practitioners become aware of its advantages, it’s likely that nerve ultrasound will play an increasingly vital role in diagnosing and managing neurological conditions.
Consider proactive steps in advocating for this method if you believe it may aid in deciphering your symptoms. Staying informed about the latest advancements can empower you as a patient. Understanding how nerve structures function and relate to paresthesia enhances not only patient engagement but also treatment outcomes.
Embracing innovative technologies like nerve ultrasound signifies progress towards more accurate diagnoses and tailored treatments. As we continue exploring these developments, patients are likely to experience improved care pathways that address their unique health challenges effectively.